26 March 2021: Animal Study
Salvianic Acid A Regulates High-Glucose-Treated Endothelial Progenitor Cell Dysfunction via the AKT/Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase (eNOS) Pathway
Yanhua Guan 12ABCDEF , Xu Wang 13ABCDEF*DOI: 10.12659/MSM.928153
Med Sci Monit 2021; 27:e928153
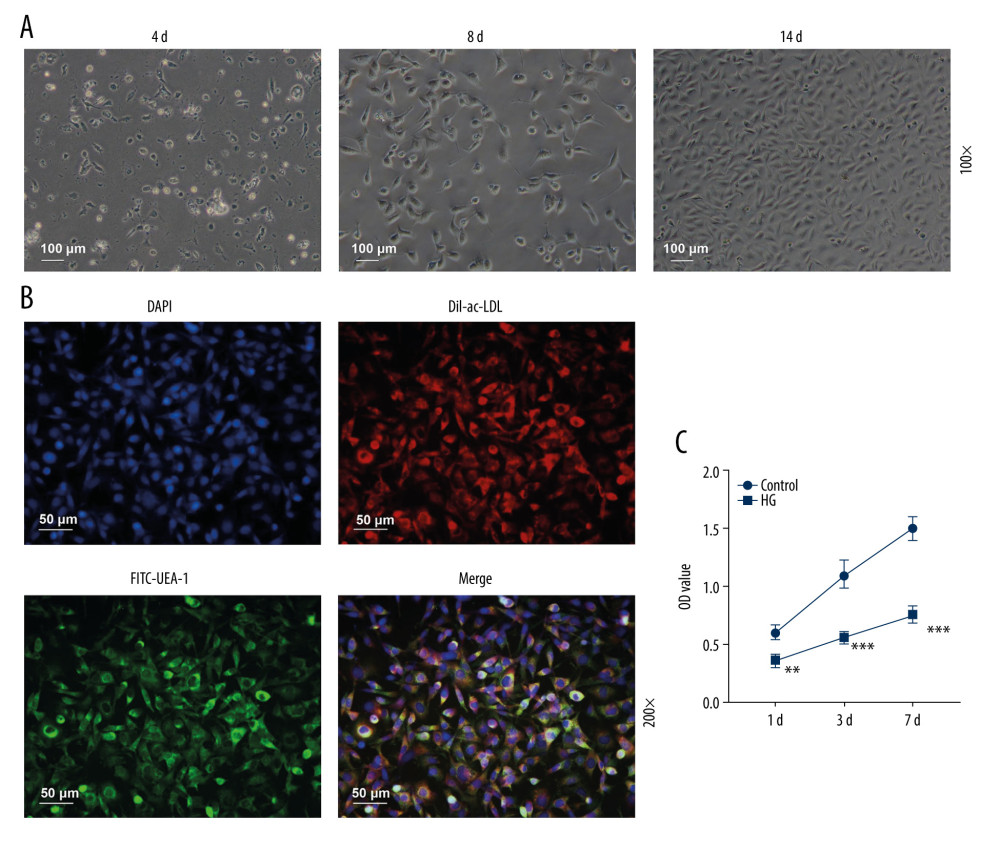
Figure 1 Identification of bone marrow-derived endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) and effects of high glucose (HG) or different concentrations of salvianic acid A (SAA) on cell viability. (A) Morphology of EPCs derived from bone marrow. Scale bar=100 μm. (B) 1,1′-Dioctadecyl-3,3,3′,3′-tetramethylindocarbocyanine-labeled acetylated low-density lipoprotein (Dil-ac-LDL) and fluorescein isothiocyanate-Ulex europaeus agglutinin-1 (FITC-UEA-1) double staining for identification of EPCs. Scale bar=50 μm. (C) 3-[4,5-Dimethylthylthiazol-2-yl]-2,5 diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay was performed to determine the effects of HG (30 mmol/L) on EPC viability at 1 day, 3 days and 7 days after culture. (Forty rats were used in this experiment.) ** P<0.01 compared to the control group.


