16 September 2022: Review Articles
Mechanisms of Myocardial Damage Due to Hyperlipidemia: A Review of Recent Studies
Zhiqi Zhang 1EF , Hongyi Wu 1F , Tao Wang 2A , Yao Liu 3F , Chun Meng 2AG*DOI: 10.12659/MSM.937051
Med Sci Monit 2022; 28:e937051
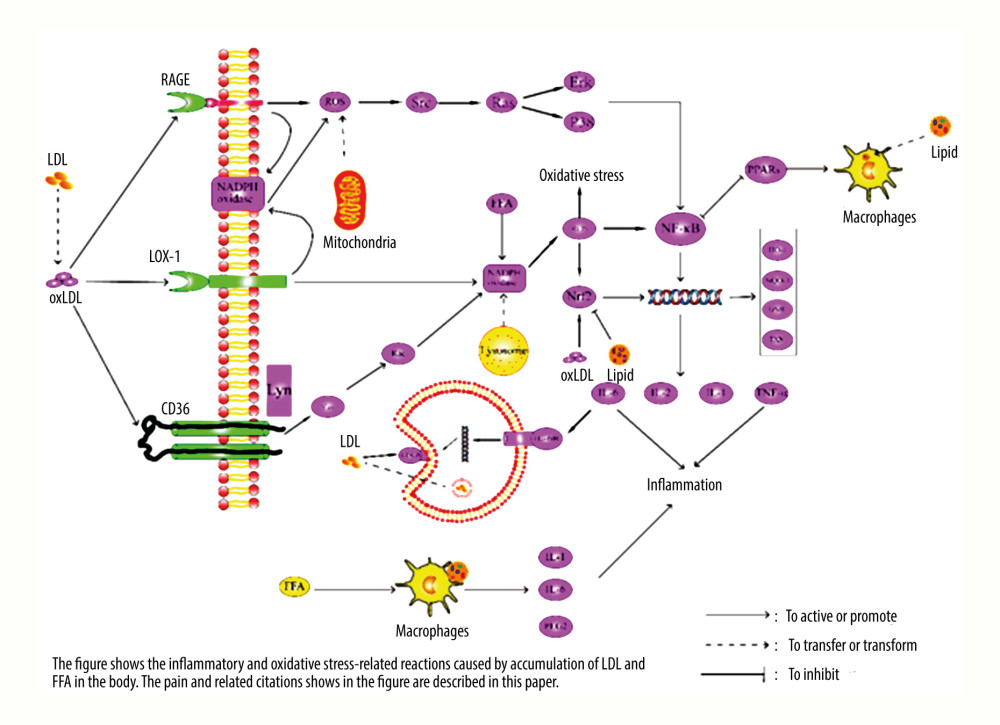
Figure 1 Pathway diagram of hyperlipidemia leading to inflammatory response and oxidative stress. LDL – low density lipoprotein; FFA – free fatty acid; ROS – reactive oxygen species; SRC – tyrosine-protein kinase Src; RAS – GTPase HRas; ERK – mitogen-activated protein kinase; P38 – P38 mitogen-activated protein kinase; VAV – guanine nucleotide exchange factor VAV; Rac – Ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate; Lyn – tyrosine-proteon kinase Lyn; TXN – thierodexin; GSH – glutathione; oxLDL – oxidized low density lipoprotein; LOX-1 – lectin-like oxidized low-density lipoprotein receptor-1; RAGE – advanced glycation end product receptor; CD36 – CD36 antigen; LDLR – LDL receptor; PPARs – peroxisome proliferators-activated receptors; HO-1 – heme oxygenate-1; NQO-1 – quinine oxidoreductase 1; NF-κB – nuclear factor-κB; Nrf2 – nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2; TNF-α – tumour necrosis factor alpha; IL – interleukin.


