12 September 2022: Editorial
Editorial: Treatment with Dual Incretin Receptor Agonists to Maintain Normal Glucose Levels May Also Maintain Normal Weight and Control Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease (MAFLD)
Ana Luisa Ordóñez-Vázquez 1 , Sofía Murúa Beltrán-Gall 1 , Shreya C. Pal 12 , Nahum Méndez-Sánchez 12*DOI: 10.12659/MSM.938365
Med Sci Monit 2022; 28:e938365
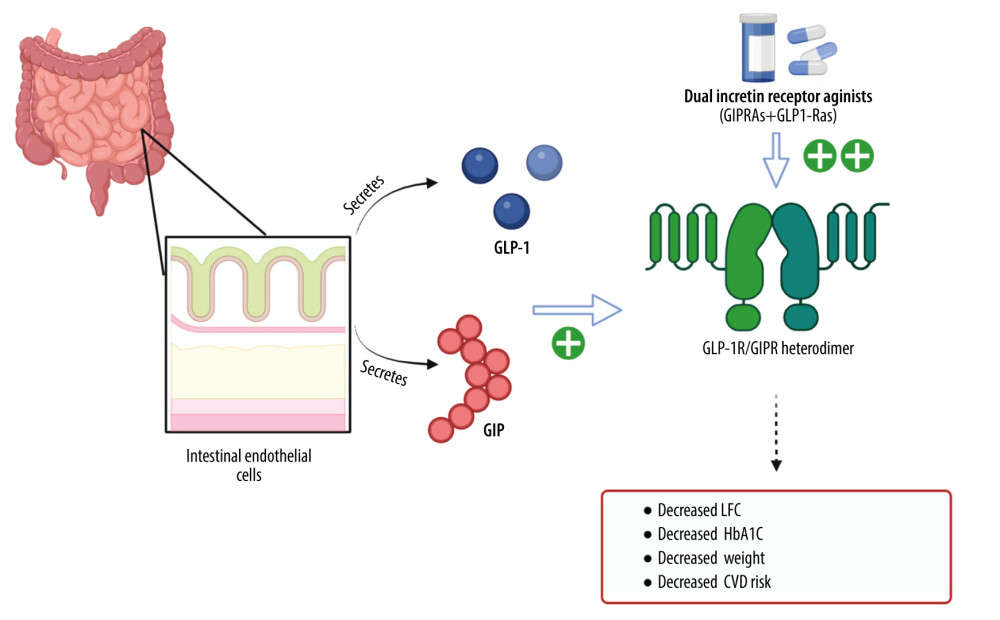
Figure 1 The mechanisms of dual incretin receptor agonists. Glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) and glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide (GIP) are the main incretins. Incretins are hormones released by endothelial cells in the intestine in response to various stimuli. Novel dual incretin receptor agonists, which include GLP-1 receptor agonists (GLP1-RAs) combined with glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide, also known as gastric inhibitory polypeptide or gastric inhibitory peptide (GIP) receptor agonists (GIPRAs), have a synergic effect. The synergy of dual incretin receptor agonists results in reduced body weight, blood glucose levels as determined by glycated hemoglobin, or hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c), total liver fat content (LFC), and a reduced risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) through increased expression of the GLP-1 receptor (GLP1R) and the GIPR (GIP receptor) heterodimer. The combined consequence of simultaneous receptor stimulation also results in improved metabolic regulation, including reduced inflammatory responses and reduced insulin resistance. The outcomes of the synergistic effects of dual incretin receptor agonists are to reduce the onset and progression of metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD).


