25 March 2022: Clinical Research
Retrospective Study of the Etiology, Laboratory Findings, and Management of Patients with Urinary Tract Infections and Urosepsis from a Urology Center in Silesia, Southern Poland Between 2017 and 2020
Zygmunt F. Gofron 1ABCDEFG* , Małgorzata Aptekorz 1CDE , Katarzyna W. Gibas 2BCDEF , Monika Kabała 1DE , Gajane Martirosian 1ABCDEFDOI: 10.12659/MSM.935478
Med Sci Monit 2022; 28:e935478
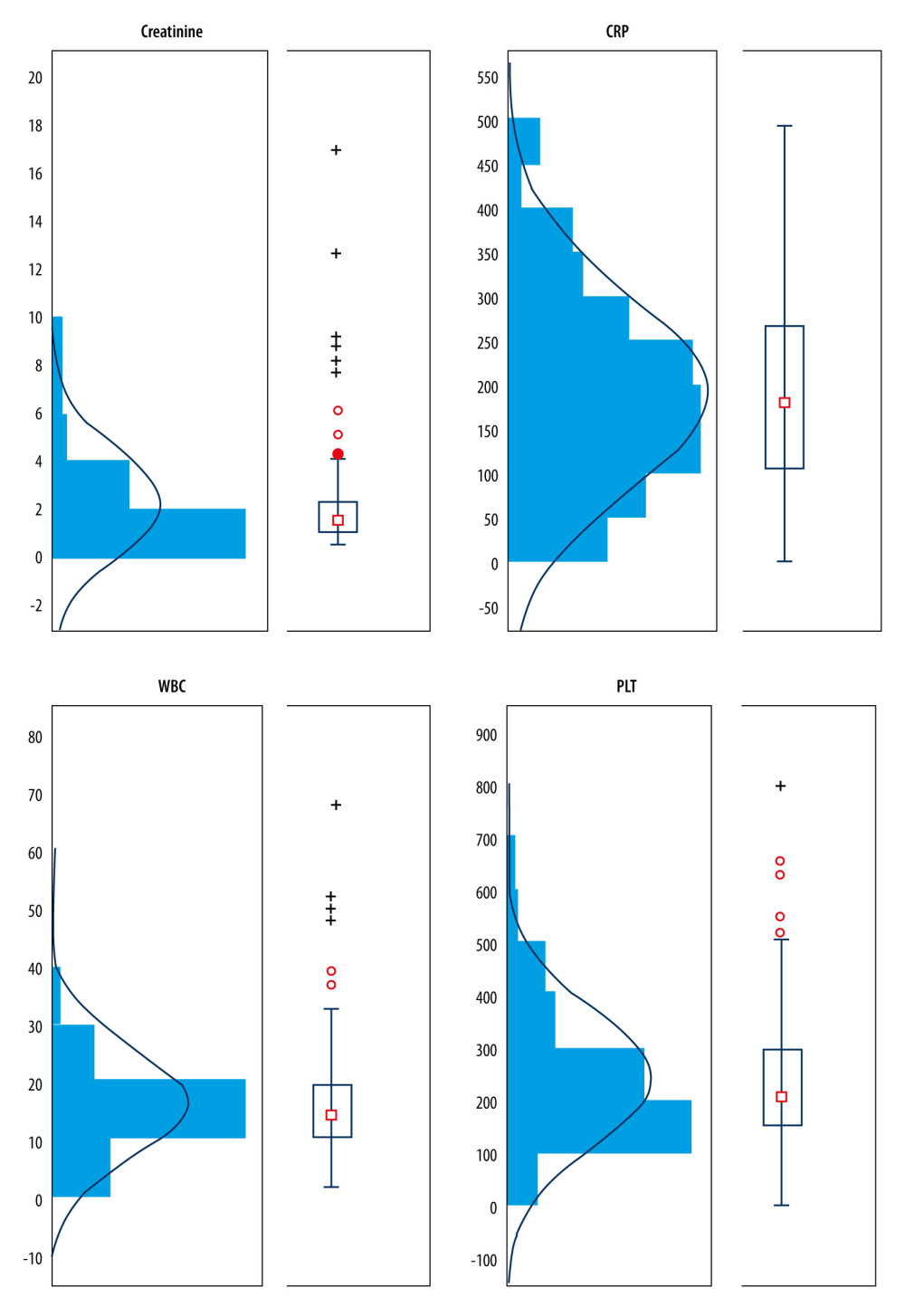
Figure 1 White blood cell count (WBC), platelet count (PLT), C-reactive protein (CRP), and creatinine levels for all patients at admission to the hospital. Creatinine levels in men were higher (median 1.68 mg/dL; range 0.77–16.81 mg/dL) than in women (median 1.47 mg/dL; range 0.59–9.22 mg/dL); this difference was statistically significant (P=0.0463). No statistically significant difference was observed between values of biochemical parameters (WBC, CRP, PLT levels) between women and men. Higher creatinine values were observed in patients with blood extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL)-positive isolates (median 1.75 mg/dL) than in patients with blood ESBL-negative isolates (median 1.44 mg/dL), and this difference was statistically significant (P 0.02). The other values for WBC, CRP, and PLT did not differ significantly in patients with sepsis caused by ESBL-positive and other isolates (Enterobacteriaceae ESBL-negative and other strains).


